選択した画像 yield strength of steel symbol 824390-Yield strength of steel symbol
Yield strength in Mechanical Engineering ( yild strɛŋkθ ) noun ( Mechanical engineering Materials) The yield strength of a bar of material is the maximum stress that can be applied along its axis before it begins to change shape Steel yield strength is the amount of stress a piece of steel must undergo in order to permanently deformThe point at which a material ceases to be elastic and becomes permanently plastic, the point at which it yields, is called its yield point The magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behaviorA yield strength of 60,000 psi or less (1) an initial linearelastic segment up to a welldefined yield strength ƒy;
Nptel Ac In Content Storage2 Courses Pdf M1l2 Pdf
Yield strength of steel symbol
Yield strength of steel symbol-Symbol Yield strength (MPa), 02 % offset Tensile strength (MPa) Elongation, A80, ≥ % Elongation, A50, ≥ % Hardness, HV Validity of the mechanical properties EN DC01 () Annealed A – 270 – 390 28 30 ≤ 105 3 months Skin passed LC ≤ 280 270 – 410 28 30 ≤ 115 Work hardened C290 0 – 380 290 – 430 18 C340 ≥ 250 340 – 490 Not requiredDepending on the type of the reinforcement bars the yield strength varies Variation can be expressed as follows Mild Steel;


Difference Between Tensile And Compressive Stress
I get datasheets with Rm, Re and Re 02%, εfailure% and Young's Modulus too and from Ashby formula, I need σf (failure strength), but it is not given in these datasheetsTo apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material σ = 0 0 0 2 × E \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×E To distinguish this approximation from other calculations, engineers sometimes call this the "offset yield stress"Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher
The Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformation occurs without increase in load In other steels and in nonferrous metals this phenomenon is not observedSymbol Unit Force and strength 22 F m N Maximum force Yield strength Proof strength Tensile strength 23 R eH MPa Upper yield strength 24 R eL MPa Lower yield strength 25 R m MPa Tensile strength 26 R p MPa Proof strength, nonproportional extension 27 R r MPa Permanent set strength 28 R t MPa Proof strength, total extension EUltimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher
Fub ultimate strength of the bolt fv characteristic shear strength fv,haz characteristic shear strength of heat affected zone fvw,d design shear resistance of the fillet weld per unit length fw characteristic strength of the weld metal fy yield stress of steel fya average yield strength fyb yield stress of the bolt fyc yield stress of columnThe 36 in 'A36' means that the steel has a minimum yield strength of 36,000 psi In this example, ASTM stands for American Society of Testing and Materials and they publish the chemical requirements for A36 steel (ie how much carbon it can have in it, as well as other alloying elements, in addition to the minimum mechanical properties it must have such as yield strength)STRUCTURAL STEEL 2 MECHANICAL PROPERTIESMECHANICAL PROPERTIES MATERIAL Yield (ReYield (RReeRe HHH) H)) ) mmiinnmin N/mmmin N/mm 2222 Thickness in mmThickness iinn mmmmin mm TensileTensile ((((RmRRmmRm) )) ) N/mmNN//mmmmN/mm 2222 ThicknessThickness in mm in mm in mm A AA A –––– min elongation min elongation



A Review Of Irradiation Effects On Mechanical Properties Of Candidate Scwr Fuel Cladding Alloys For Design Considerations


Q Tbn And9gctkrzf52tulw Hck4iec8kqmmvrheff2kzrugh6dmtmgku6pybl Usqp Cau
For structural design according to Eurocode 3 (EN), the nominal values of the yield strength fy and the ultimate strength fu for structural steel are obtained as a simplification from EN Table 31, which is reproduced above in tabular format The provided values for fy and fu are nominal valuesSSSS= Structural steel symbol Min Yield strength in N/mm 2 R e Notch toughness (J)Notch toughness ((JJ)) (J) MinMMiinnMin 2277 JJ27 J 27 J JJRRJR JR JJ00J0 J0 JJ22J2 J2 JJ33J3 J3 JJ44J4 J4 MinMMiinnMin 40 J4400 JJ40 J KRKKRRKR K0KK00K0 K2KK22K2 K3KK33K3 K4KK44K4 TempTemp °C°°CC°C 0000The units are N/mm2 or MPa, the symbol is σbc ④ Yield Strength It refers to the stress of the metal sample during the stretching process, when the load no longer increases and the sample continues to deform The unit is N/mm2 or MPa symbol is σs The yield strength is the pressure value of the yield point


The Effect Of Elements On The Properties Of Stainless Steels
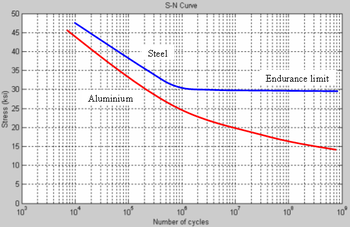


Fatigue Limit Wikipedia
Yield strength is mainly used there Another criterion might be based on the instances found in a google search "Yield strength" produces results, "yield stress" produces resultsPipeline Restart Loop Yield Strength Restart Loop with 2 pumps for blending and/or sectionwise mixing Deposition of complex and heavy organic compounds in crude and heavy oil can cause a number of severe problems up to pipeline blocking(2) a relatively flat yield plateau up to the onset of strain hardening, the strain at which is designated ε sh;



Monotonic Mechanical Properties Of 34crnimo6 Steel Download Scientific Diagram



Metal Mechanical Properties Chart Shear Strength Tensile Strength Yield Strength Machinemfg
Yield strength σ y Yield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding a material deforms permanently;The ultimate tensile strength of mild steel varies from 600 to 800 N/mm 2 High Tensile Steel The ultimate tensile strength of high tensile steel is around 00 N/mm 2 06 Hardness Hardness is the ability of a material to resist the penetration by a harder bodyThe allowable design stress in steel should not be more than 40% of the minimum yield strength of steel 8635 Maximum driving stress Maximum driving stress for steel piles = 09 f y (for both tension and compression) f y = yield strength
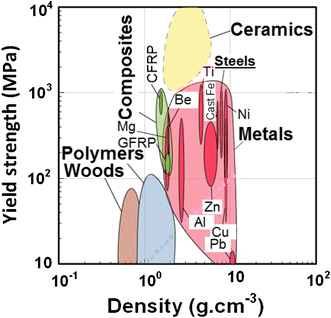


Low Density Steels Springerlink
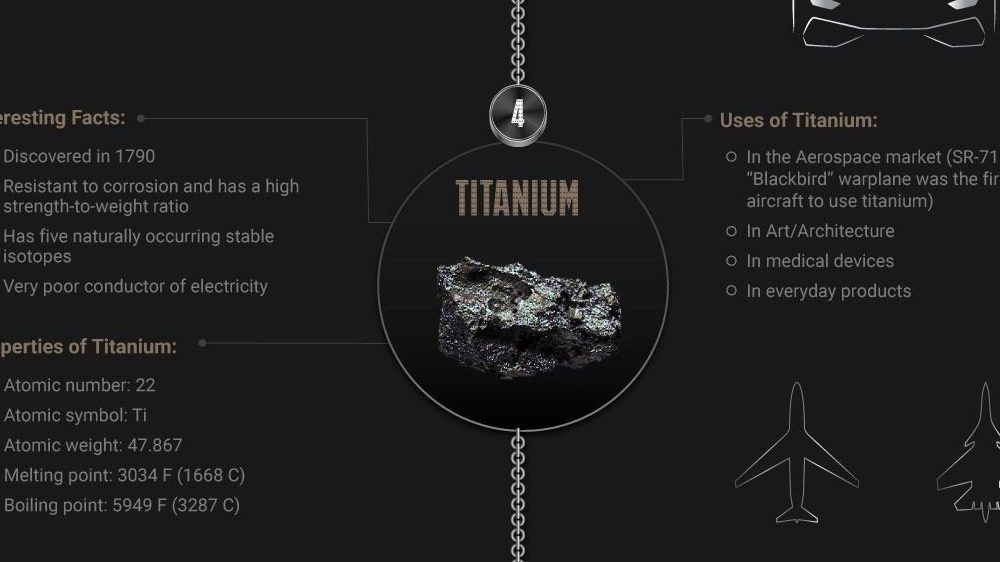


Prove Your Metal Top 10 Strongest Metals On Earth Visual Capitalist
Yield Strength Tensile Strength % Elong MPa (ksi) MPa (ksi) Steel Alloy A36 Hot rolled 2 250 (32 36) 400 500 (58 725) 23 Steel Alloy 10 Hot rolled 210 (30) (min) 380 (55) (min) 25 (min) Steel Alloy 10 Cold drawn 350 (51) (min) 4 (61) (min) 15 (min) Steel Alloy 10 Annealed (@870 °C) 295 (428) 395 (573) 365Min Yield Strength (psi) Min Tensile Strength (psi) 307A Low carbon steel 1/4" thru 4"» Axial Strain An axial bar of length L, and crosssectional area A, subjected to tensile force P, elongates by an amount, DThe change in length divided by the initial length is termed ENGINEERING STRAIN (or simply strain)The symbol used for engineering strain in most texts is e (epsilon) The strain in an axially loaded bar is defined as



Solved The Symbol Of Aisusae 4340 Treatment Steel Is 34cr Chegg Com
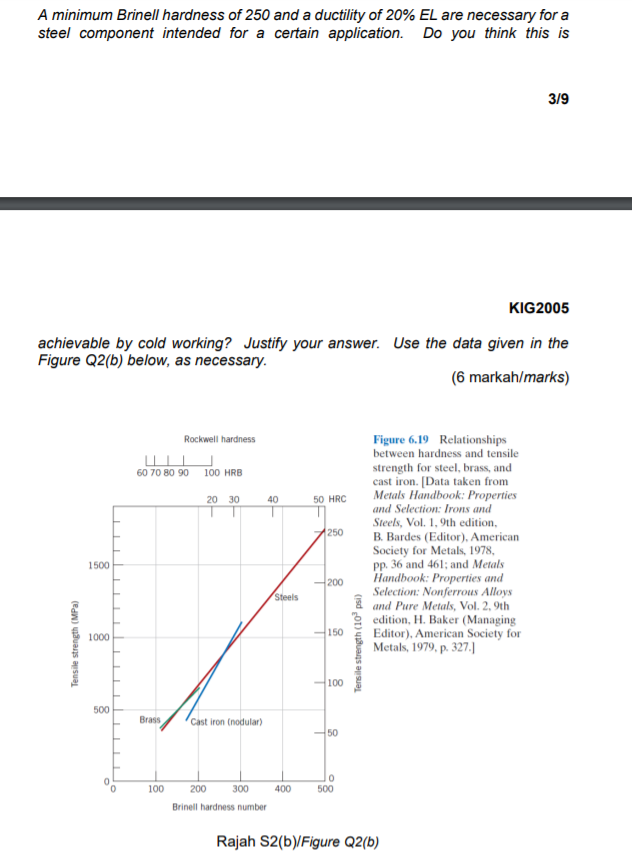


The Hall Petch Equation Yield 0 K D 1 2 Shows T Chegg Com
Thermal stress and force;For example, aluminum has a yield strength of 14,000 pounds per square inch (or psi), copper has a yield strength of 10,000 psi, and steel, being an alloy of several different materials, has aW – Weathering steel (atmospheric corrosion resistant)


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora



Yield Engineering Wikipedia
Features of European steel and alloy database Steel numbers Listing of all steels according to steel classification standard EN Steel and cast iron standards Listing oS355J0 Steel Plates The symbol S mainly stands for structural steel, 355 is minimum yield strength and grade S355J0 can easily withstand impact energy of 27J at 0 degree Celsius These steel plates have high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, weldability, dimensional accuracy, durability, machinability, and long service lifeYield Strength Tensile Strength % Elong MPa (ksi) MPa (ksi) Steel Alloy A36 Hot rolled 2 250 (32 36) 400 500 (58 725) 23 Steel Alloy 10 Hot rolled 210 (30) (min) 380 (55) (min) 25 (min) Steel Alloy 10 Cold drawn 350 (51) (min) 4 (61) (min) 15 (min) Steel Alloy 10 Annealed (@870 °C) 295 (428) 395 (573) 365
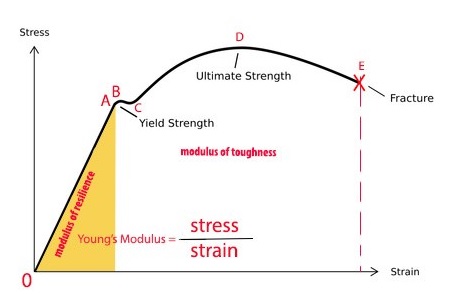


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve



Materual Is Designation 19
A yield strength of 60,000 psi or less (1) an initial linearelastic segment up to a welldefined yield strength ƒy;Symbol Yield strength (MPa), 02 % offset Tensile strength (MPa) Elongation, A80, ≥ % Elongation, A50, ≥ % Hardness, HV Validity of the mechanical properties EN DC01 () Annealed A – 270 – 390 28 30 ≤ 105 3 months Skin passed LC ≤ 280 270 – 410 28 30 ≤ 115 Work hardened C290 0 – 380 290 – 430 18 C340 ≥ 250 340 – 490 Not required141 Marking of Steel The most common type of marking in Czech republic is by fivedigits number (eventually sixdigits), for example 10 335,or 11 373, where first two digits material group sign 10 building steel, 11 machine steel second two digits for steels from group 10 33 1/10 of yield strength in MPa
.jpg)


Structural Steel S235 S275 S355 Chemical Composition Mechanical Properties And Common Applications
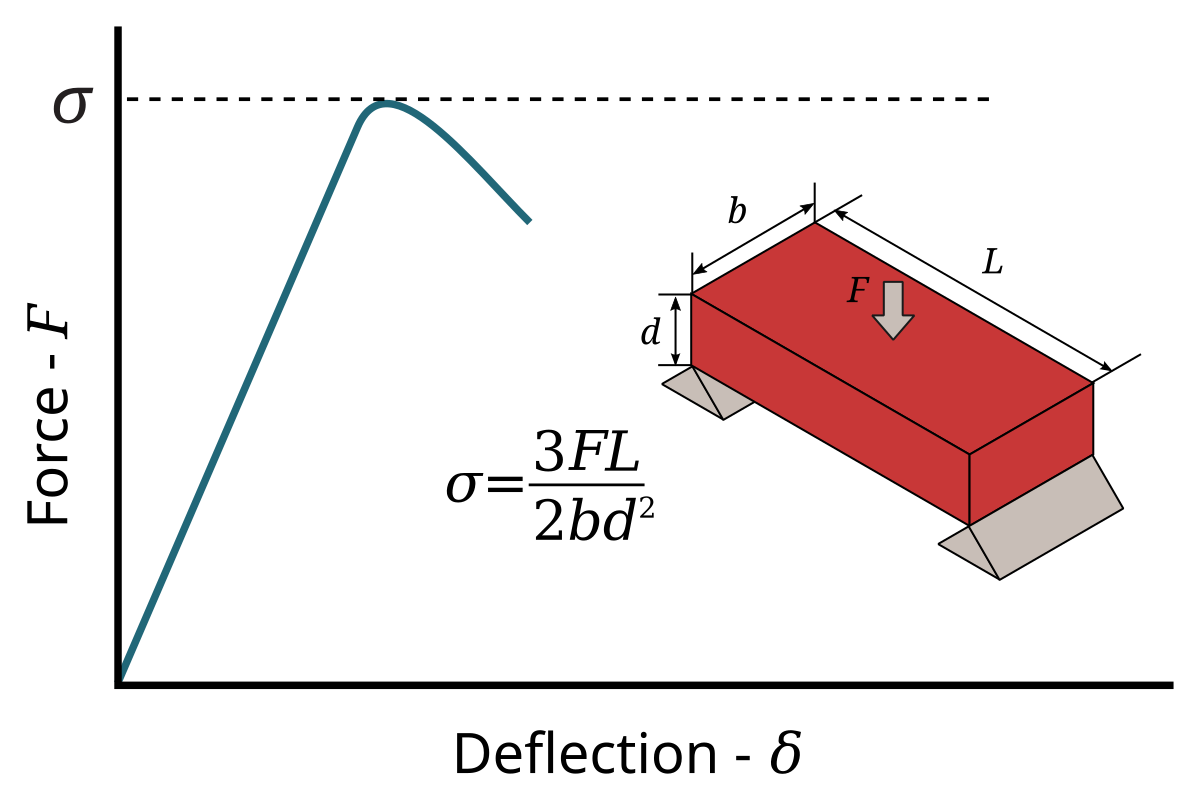


Flexural Strength Wikipedia
141 Marking of Steel The most common type of marking in Czech republic is by fivedigits number (eventually sixdigits), for example 10 335,or 11 373, where first two digits material group sign 10 building steel, 11 machine steel second two digits for steels from group 10 33 1/10 of yield strength in MPaThe 02% proof strength In some steels, for example cold worked steels, no yield effect is observed, the stressstrain plot showing a continuous curve after the linear elastic portion (Figure 2) In these steels, yield strength is always defined as the 02% proof strength The tensile strength/yield strength ratio (R m/R e) is a measure of a steel's abilityTensile strength of steel will show us how much tensile stress the steel can withstand until it leads to failure in two ways ductile or brittle failure Ductile failure – think of this as the preliminary stage of failure, where it is pushed beyond the yield point to permanent deformation


Www Aisc Org Globalassets Aisc Manual 15th Ed Ref List Specification For The Design Of Steel Hollow Structural Sections Pdf



An Integrated Model For Austenite Yield Strength Considering The Influence Of Temperature And Strain Rate In Lean Steels Sciencedirect
1 Hotrolled high yield strength bars 2 Cold worked high yield strength bars The (2) type of steel is also called as CTD (Cold Twisted Deformed) bars or Tor steel and are available in two grades Deformed bars are represented by symbol # 1 Fe 415 or Tor 40 2 Fe 500 or Tor 50 A twisted deformed bar has about 50% higher yield stress than plain barsTo apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material σ = 0 0 0 2 × E \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×E To distinguish this approximation from other calculations, engineers sometimes call this the "offset yield stress"Minimum Tensile Yield Strength X95 95,000 G105 105,000 S135 135,000 V150* 150,000
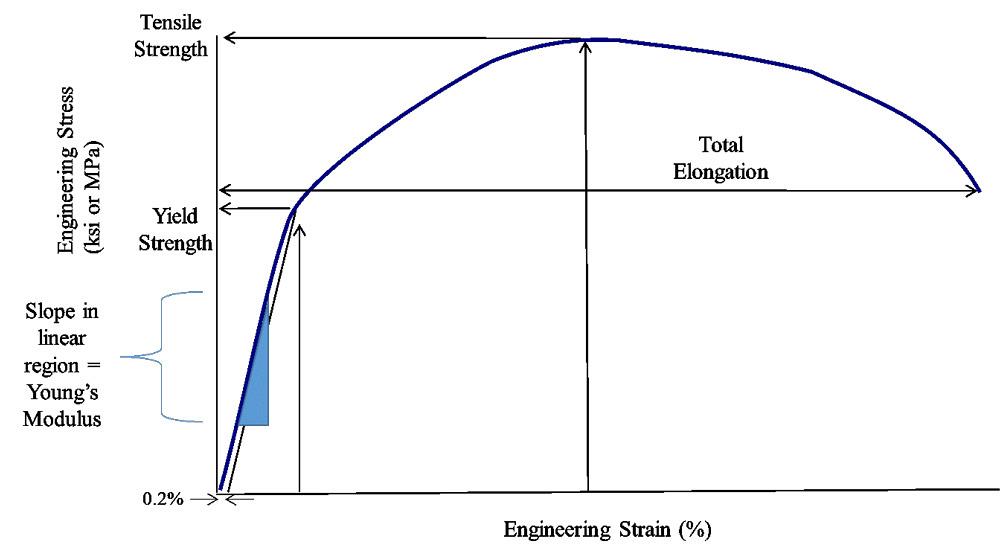


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



1 Ks Standards For Steel Reinforcement Rebar Standards For Steel Reinforcement Rebar Table 2 Mechanical Properties Symbol Of Kinds Yield Point Or Yield Strength N Tensile Pdf Document
235 – related to the minimum yield strength of the steel (tested at a thickness of 16 mm) J2/K2/JR/JO – material toughness in relation to the Charpy impact or 'V'notch test methodology;And (3) a rounded strainhardening segment ASTM Designation and Type Available Grades Minimum Yield Strength, ƒy (psi)S – denotes the fact that it is structural steel;



Fastenerdata Fastener Tensile Strength 10 N Fastener Specifications



Metals Free Full Text Property Optimization In As Quenched Martensitic Steel By Molybdenum And Niobium Alloying Html
The main difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that yield strength is the minimum stress under which a material deforms permanently, Strain is usually given the symbol The graph below shows the stressstrain curve for a typical ductile material such as steelAnd (3) a rounded strainhardening segment ASTM Designation and Type Available Grades Minimum Yield Strength, ƒy (psi)Other articles where Yield strength is discussed materials testing Radiation Tensile and yield strength of a type of carbonsilicon steel increase with exposure to neutron radiation, although elongation, reduction in area, and probably fracture toughness apparently decrease with exposure Certain wood/polymeric composite materials are even prepared by a process that employs radiation



Relationship Between The Grain Size And The Yield Strength A And The Download Scientific Diagram



Question 2 The Symbol Of Aisusae 4340 Treatment S Chegg Com
For example, aluminum has a yield strength of 14,000 pounds per square inch (or psi), copper has a yield strength of 10,000 psi, and steel, being an alloy of several different materials, has aF y = 250 N/mm 2 Tor Steel;Yield Strength Tensile Strength % Elong MPa (ksi) MPa (ksi) Steel Alloy A36 Hot rolled 2 250 (32 36) 400 500 (58 725) 23 Steel Alloy 10 Hot rolled 210 (30) (min) 380 (55) (min) 25 (min) Steel Alloy 10 Cold drawn 350 (51) (min) 4 (61) (min) 15 (min) Steel Alloy 10 Annealed (@870 °C) 295 (428) 395 (573) 365



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
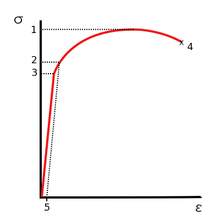


Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia
Mn nominal flexure strength with the full section at the yield stress for LRFD beam design (lbft, kipft, Nm, kNm) Mp (also Mult) internal bending moment when all fibers in a cross section reach the yield stress (lbft, kipft, Nm, kNm) Mu maximum moment from factored loads for LRFD beam design (lbft, kipft, Nm, kNm)Steel bars are clear, free from loose mil scales, dust and loose rust coats of paints, oil or other coatings which may destroy or reduce bond strength Steel bars should be stored in such a way as to avoid distortion and to prevent deterioration and corrosion Steel bars should not be clean by oily substance to remove the rustF y = 460 N/mm 2 TMT bars;


Nptel Ac In Content Storage2 Courses Pdf M1l2 Pdf
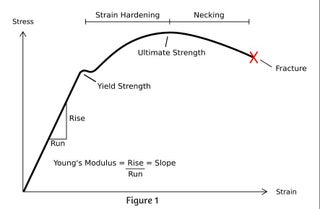


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables
The structural steel's yield strength measures the minimum force needed to create a permanent deformation in the steel The naming convention used in European Standard EN relates to the minimum yield strength of the steel grade tested at 16 mm thickThis assumes that yield occurs when the shear stress exceeds the shear yield strength τ = σ 1 − σ 3 2 ≤ τ y {\displaystyle \tau ={\frac {\sigma _{1}\sigma _{3}}{2}}\leq \tau _{y}\,\!} Total strain energy theory – This theory assumes that the stored energy associated with elastic deformation at the point of yield is independent of the specific stress tensorIn European Standards for structural carbon steels (including weathering steel), the primary designation relates to the yield strength, eg S355 steel is a structural steel with a specified minimum yield strength of 355 N/mm² The product standardsalso specify the permitted range of values for the ultimate tensile strength (UTS)


Table Of Material Properties For Structural Steel S235 S275 S355 S4



What Is Q345 Steel Www Steeljrv Com
Mild steel bars are also known as Fe 250 because the yield strength of this steel is 250N/mm 2 The stressstrain curve for mild steel is given inFig 11 It shows a clear, definite yield point Although mild steel bars are very ductile, they are not preferred over high yield strength deformed bars because of their less strength and weak bondTensile Strength ,500 PSI 555 MPA Yield Strength 59,000 PSI 410 MPA Elongation 36% 1016 AWS A54 $1495 3/32 1 lb Pack $7800 3/32 8 lb Pack $9750 3/32 10 lb Pack cast form The weld deposit is fully austenitic, $1295 1/8 1 lb Pack $9000 1/8 10 lb PackThe rod in the example above is 2 m long and made of steel with Modulus of Elasticity 0 GPa (0 10 9 N/m 2) The change of length can be calculated by transforming (3) to dl = σ l o / E = (127 10 6 Pa) (2 m) / (0 10 9 Pa) = m = 127 mm How to calculate radial contraction ;



Characteristic Strength Of Materials Characteristic Load Or Ultimate Load



European Designation System For Steel 13th Edd Steel Strength Of Materials
(2) a relatively flat yield plateau up to the onset of strain hardening, the strain at which is designated ε sh;The allowable design stress in steel should not be more than 40% of the minimum yield strength of steel 8635 Maximum driving stress Maximum driving stress for steel piles = 09 f y (for both tension and compression) f y = yield strengthF y = 500 N/mm 2 There are other types of bars that have yield strength more than the specified value above also


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau



Loading Rates And Tensile Properties Fracture Toughness Twi



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc
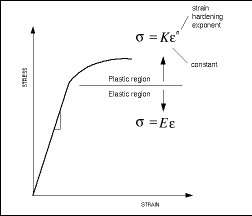


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers
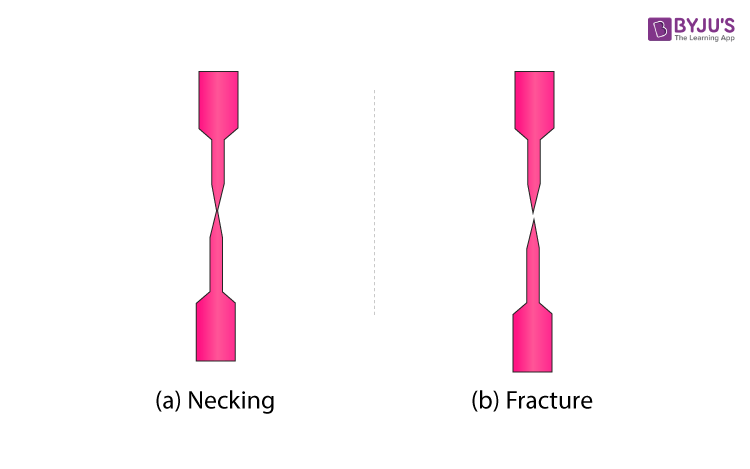


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
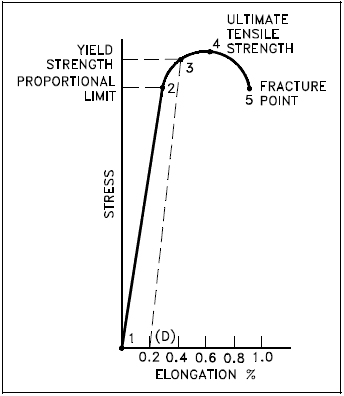


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library


1
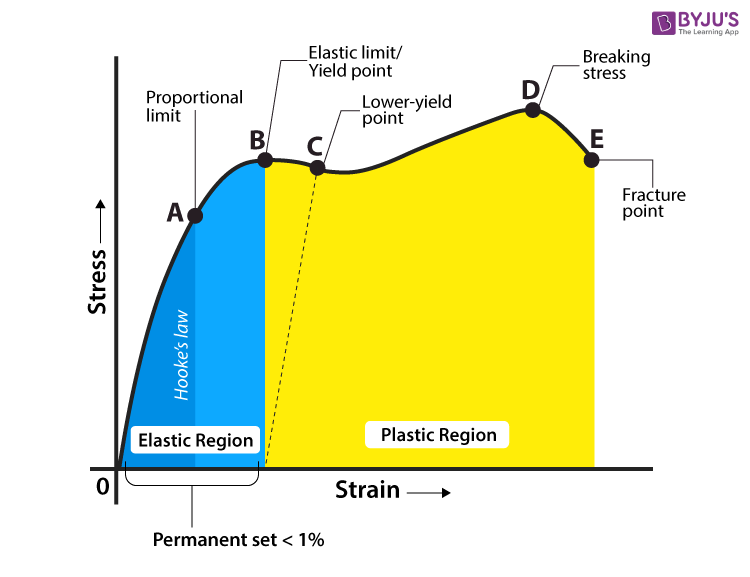


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Loading Rates And Tensile Properties Fracture Toughness Twi



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


What Is Fe 415 In A Steel Structure Quora



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
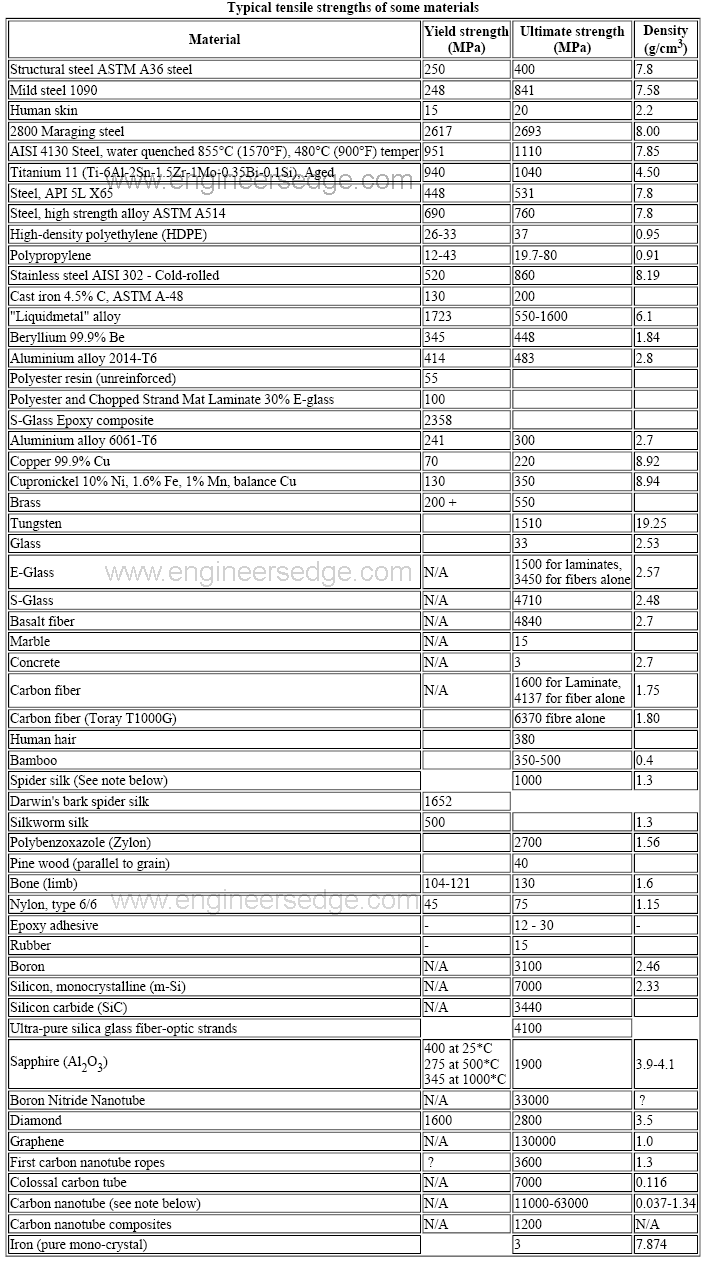


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



High Tensile Steel An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Pdf Mechanical Properties Of Cold Drawn Low Carbon Steel For Nail Manufacture Experimental Observation


Solved The Symbol Of Aisusae 4340 Treatment Steel Is 34cr Chegg Com
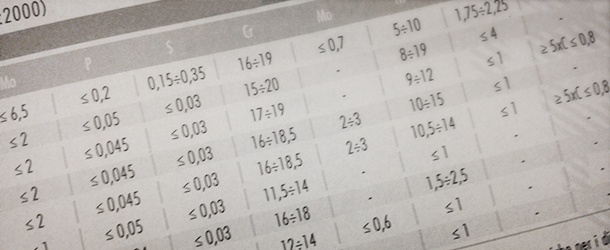


Standards And Tables
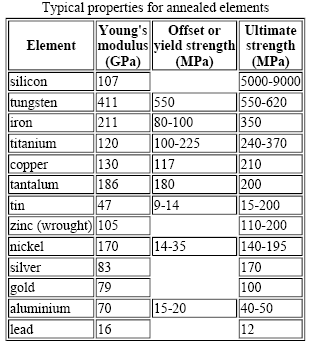


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Yield Strength Of Cold Worked Type 316 Stainless Steel Irradiated Download Scientific Diagram


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Mechanical Properties Of Steel Sm45c Download Table



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Tensile Strength Rm Definitions Of Mechanical Properties For Screws Bossard Group



Yield Strength R Sub El Sub N Mm Sup 2 Sup Bossard Group



Metal Mechanical Properties Chart Shear Strength Tensile Strength Yield Strength Machinemfg


Difference Between Tensile And Compressive Stress
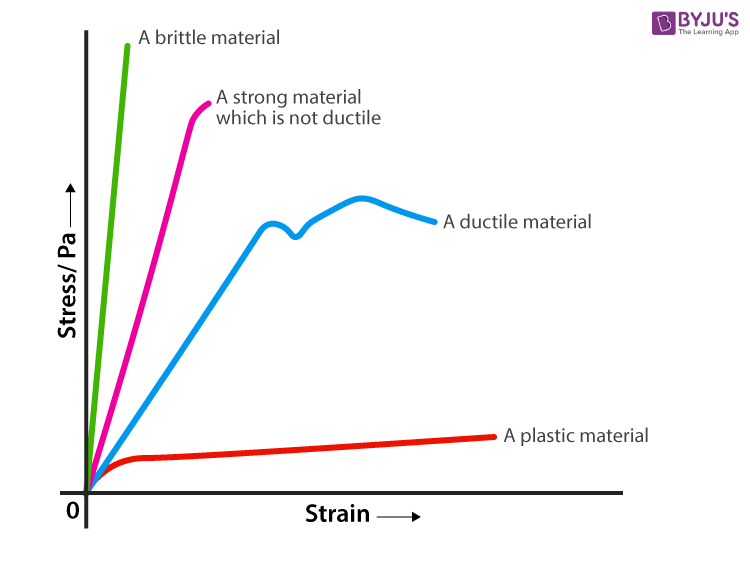


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Weibull Plots Of The Tensile Strength Of Five Structural Alloys Al Download Scientific Diagram


Yield Strength Of Steel Formula



Mechanical Properties Of Crankshaft Material And The Standard Value For Download Scientific Diagram



Physical And Mechanical Properties Of The Wind Turbine Model Download Table



Flexural Strength Wikipedia
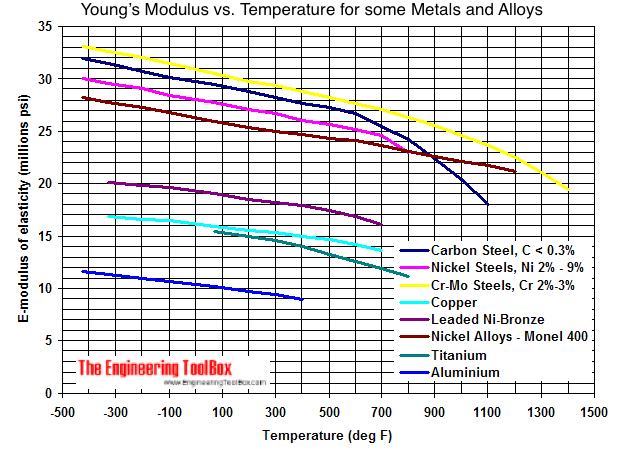


Young S Modulus Of Elasticity For Metals And Alloys



Reinforcing Material Charectristic Strength And Types Of Steel Reinforcement


What Is The Standard Value Of Yield Stress Of Steel Bars Quora



Solved Question 11 If The Compressive Strength Of Concret Chegg Com


Http Faculty Legacy Arch Tamu Edu Anichols Index Files Courses Ends231 Symbols Pdf


A Yield Strength Filled Symbols And Ultimate Tensile Strength Open Download Scientific Diagram



Strength Of Materials Wikipedia



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Material Properties Of Destroyed Material Medium Carbon Steel 1030 Download Table
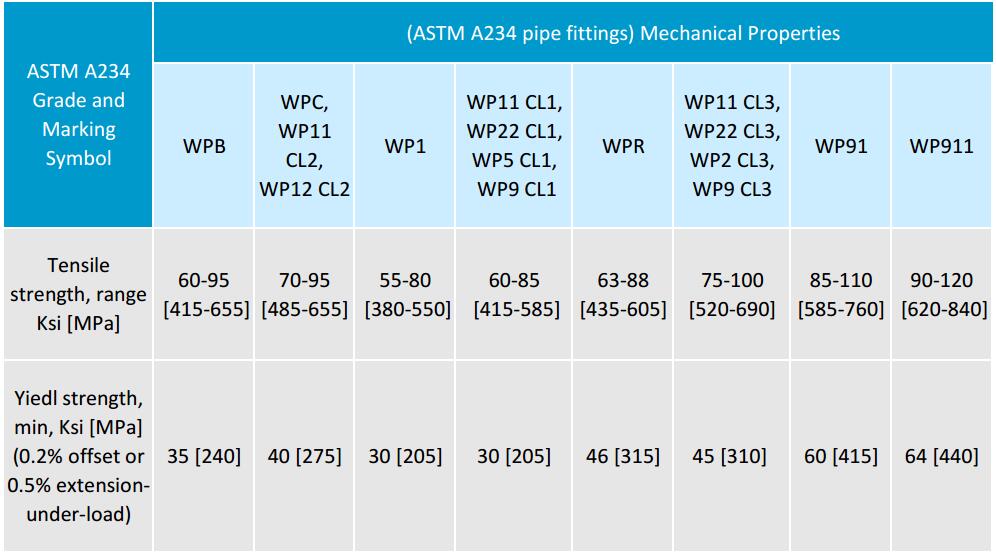


Astm 34 Wpb Steel Pipe Fittings Standard Specification



What Is Fe 415 In A Steel Structure Quora


Constructalia Arcelormittal Com Files 25 The Right Choice Of Steel Ver2 2f527a0e4146abc58c2c4c8015ccca Pdf



Experimental And Numerical Investigation Of Sup12 Steel Coil Spring Topic Of Research Paper In Materials Engineering Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
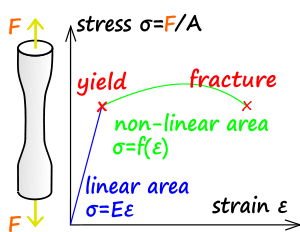


Strength Of Materials Wikipedia



Why Cold Steel Is Brittle Knife Steel Nerds



Loading Rates And Tensile Properties Fracture Toughness Twi



Nickel Definition Properties Symbol Uses Facts Britannica



Higher Grade Reinforcement Path To Future



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel


Generic Mmpds Mechanical Properties Table



Solved 5 What Does The Structural Material 350w Mean A Chegg Com


Simple Stress



Mechanical Properties Of Steel Sm45c Download Table


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia



Failure Strength Sf From Re Rm R 0 2 E And Efailure



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory


Twip Trip Ahss Stainless Steel High Mn Steel Manganese Austenite Ultra Fine Grained Steel Ufg Steel
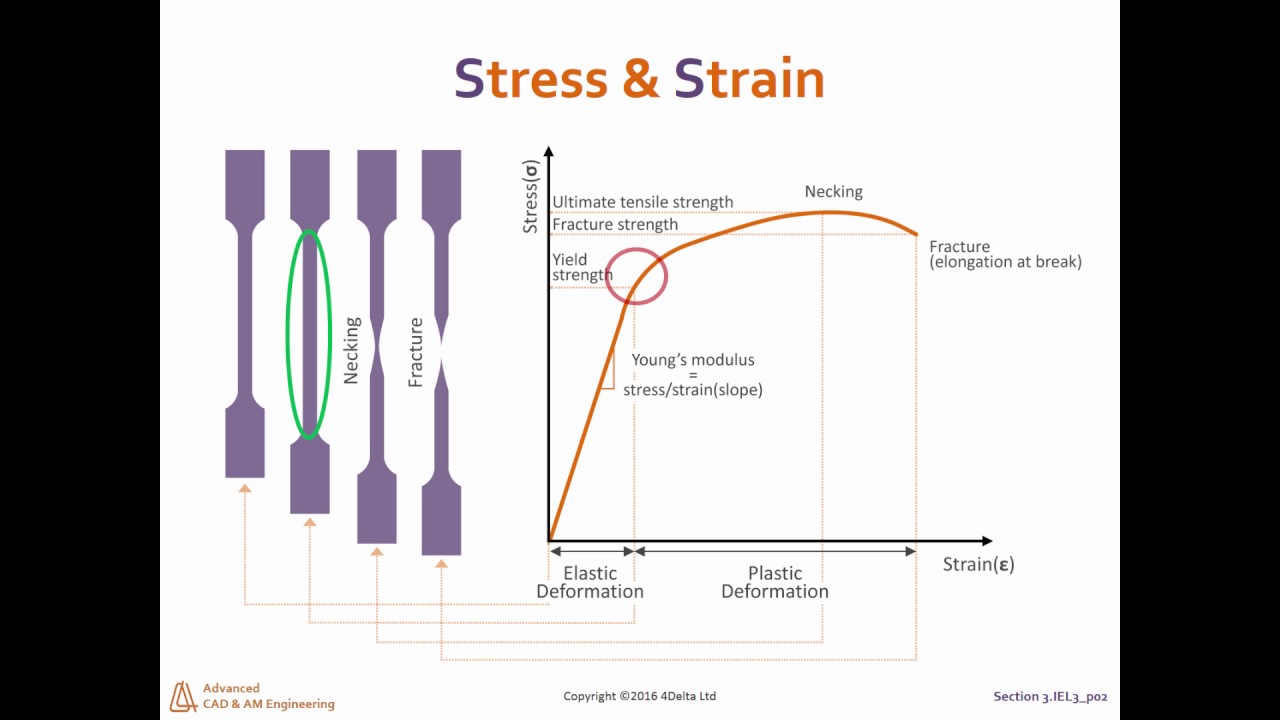


Yield Stress Yield Strenght Youtube



Yield Strength Of Steel
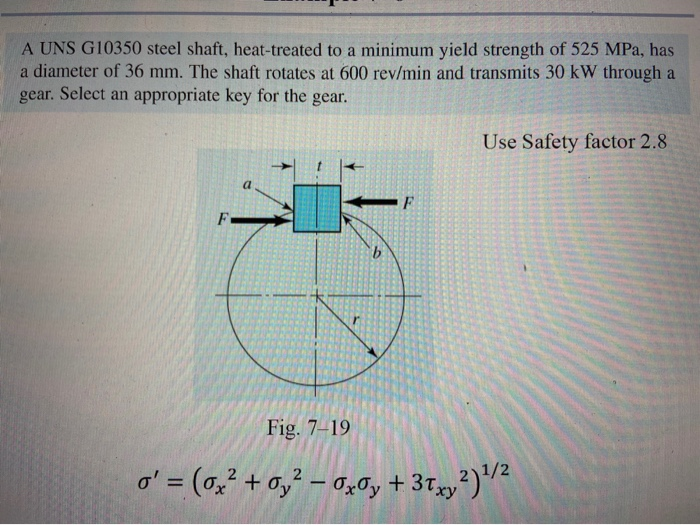


Solved A Uns G Steel Shaft Heat Treated To A Minimu Chegg Com



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve



Loading Rates And Tensile Properties Fracture Toughness Twi
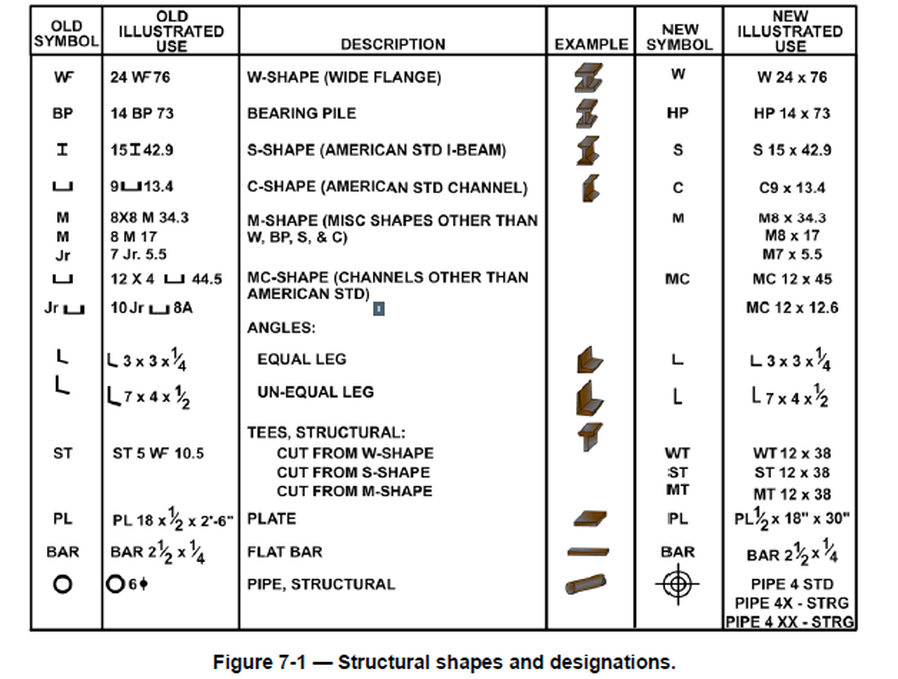


Structural Steel Drawings Computer Aided Drafting Design



Grade 8 Vs 10 9 High Tensile Bolts Alloy Steel Class 12 9 Studs


Web Adanabtu Edu Tr Files Iyilmaz Duyuru Dosya Me 7 E2 80 93 chapter 3 P3 Pdf
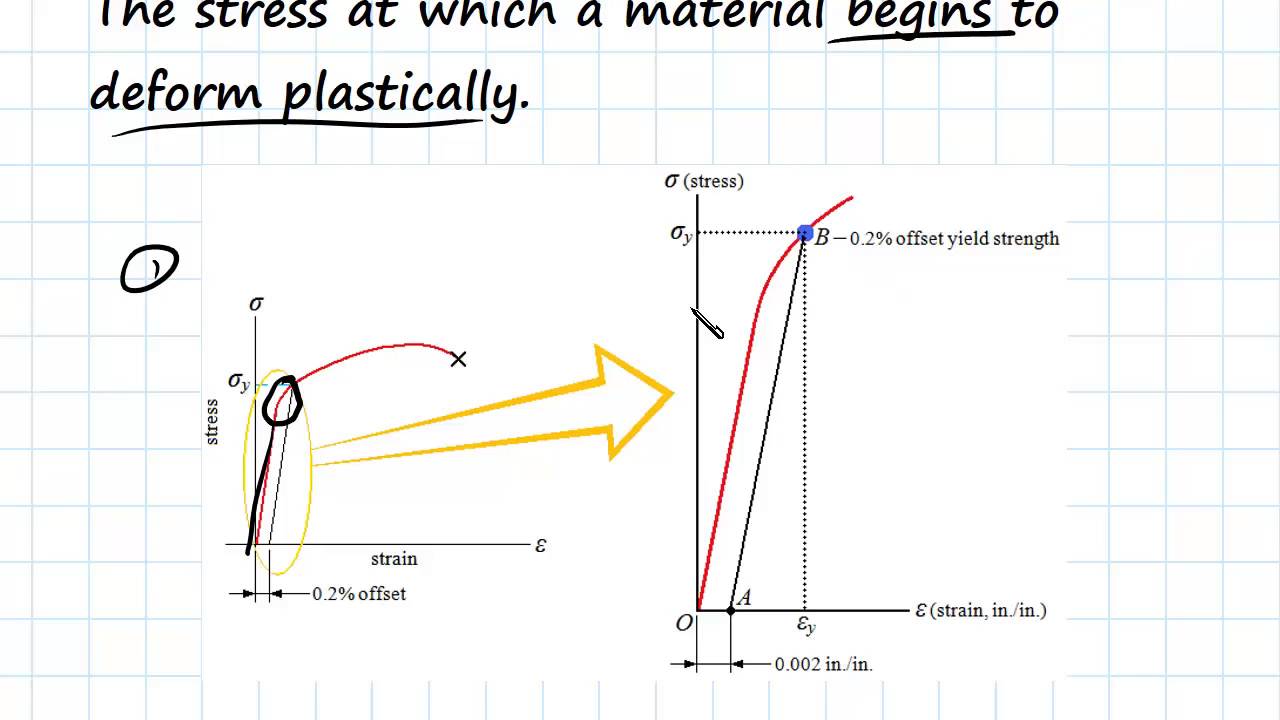


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube


Static1 Squarespace Com Static 514c9dcde4b0b45af33e225b T e4bfd71aabf Twr92 2 Pdf
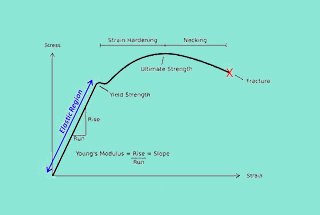


Mechanical Properties Of Sheet Metal Materials Complete List Machinemfg


コメント
コメントを投稿